로그인
login → mainController → CurrentUser - Annotation → UserAccount
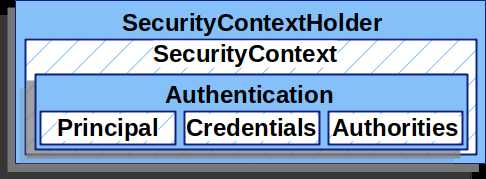
Authentication Components
SecurityContextHolder
- where Spring Security stores the details of who is authenticated.
-
a heart of Spring Security’s authentication model
-
빈 SecurityContext 만든다
SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
-
authentication token 을 만든다
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
- SecurityContext를 SecurityContextHolder에 설정한다
// AccountService
public void login(Account account) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
new UserAccount(account),
account.getPassword(),
List.of(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"))); // 권한 <- 정석 대로는 authenticationManager를 통해서 함
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
context.setAuthentication(token);
}
// UserAccount.java
@Getter
public class UserAccount extends User {
private Account account;
public UserAccount(Account account) {
super(account.getNickname(), account.getPassword(), List.of(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER")));
this.account = account;
}
}Authentication
The Authentication serves two main purposes within Spring Security:
- An input to AuthenticationManager to provide the credentials a user has provided to authenticate. When used in this scenario,
isAuthenticated()returnsfalse. - Represents the currently authenticated user. The current
Authenticationcan be obtained from the SecurityContext.
The Authentication contains:
principal- identifies the user. When authenticating with a username/password this is often an instance of UserDetails.credentials- Often a password. In many cases this will be cleared after the user is authenticated to ensure it is not leaked.authorities- the GrantedAuthority`s are high level permissions the user is granted. A few examples are roles or scopes.
Test
- 인증된 사용자로 기능 테스트하기
- 테스트할 때 사용할 사용자를 만든다
@WithSecurityContext
- 유연한 형태
- SecurityContext 는 JUnit @Before 시점에 설정됨
// StudySettingsControllerTest.java
@Test
@WithAccount("jieun")
@DisplayName("스터디 소개 수정 폼 조회 - 실패 (권한 없는 유저)")
void updateDescriptionForm_fail() throws Exception {
Account accountUnauthorized = accountFactory.createAccount("accountUnauthorized");
Study study = studyFactory.createStudy("test-study", accountUnauthorized);
mockMvc.perform(get("/new-study"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("study/form"))
.andExpect(model().attributeExists("account"))
.andExpect(model().attributeExists("studyForm"));
}// WithAccount.java
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@WithSecurityContext(factory = WithAccountSecurityContextFactory.class)
public @interface WithAccount {
String value();
}
// WithAccountSecurityContextFactory.java
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class WithAccountSecurityContextFactory implements WithSecurityContextFactory<WithAccount> {
private final AccountService accountService;
@Override
public SecurityContext createSecurityContext(WithAccount withAccount) {
String nickname = withAccount.value();
SignUpForm signUpForm = new SignUpForm();
signUpForm.setNickname("jieun");
signUpForm.setEmail("jieun@icloud.com");
signUpForm.setPassword("12341234");
accountService.processNewAccount(signUpForm);
UserDetails principal = accountService.loadUserByUsername(nickname);
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, principal.getPassword(), principal.getAuthorities());
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication((authentication));
return context;
}
}@BeforeEach
// studyTest.java
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
study = new Study();
account = new Account();
account.setNickname("jieun");
account.setPassword("12341234");
userAccount = new UserAccount(account);
}