https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/web.html
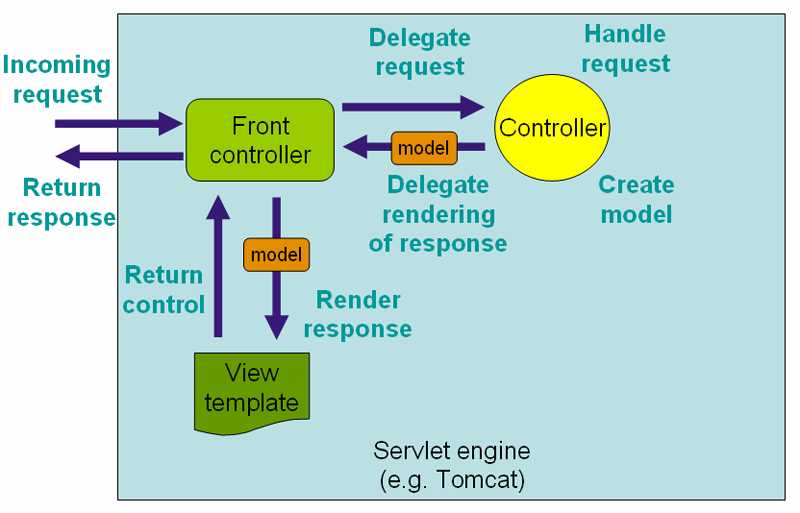
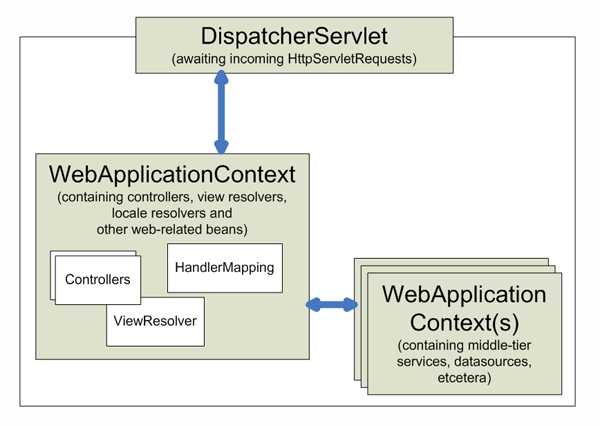
Spring MVC Framework
- designed around a central Servlet that dispatches requests to controllers
- facilitates the development of web applications.
- use any object as a command or form-backing object (mapped with java back end)
@Controller
public
class MainController {
// dynamically get principal
@GetMapping("/")
public String home(@CurrentAccount Account account, Model model) {
if (account != null) {
model.addAttribute(account);
}
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "login";
}As you can see, the @Controller and @RequestMapping annotations allow flexible method names and signatures.
In this particular example the method accepts a Model and returns a view name as a String.
@Controller and @RequestMapping and a number of other annotations form the basis for the Spring MVC implementation.
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.2.x/spring-framework-reference/html/mvc.html
Reference
Servlet
A technology used to generate dynamic content. (e.g. CGI)
An object that receives a request and generates a response based on that request.
A servlet is a Java programming language class that is used to extend the capabilities of servers that host applications accessed by means of a request-response programming model. Although servlets can respond to any type of request, they are commonly used to extend the applications hosted by web servers. For such applications, Java Servlet technology defines HTTP-specific servlet classes.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jakarta_Servlet
https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/5/tutorial/doc/bnafd.html
User Scenario
-
Assume that a user requests to visit a URL.
- The browser then generates an HTTP request for this URL.
- This request is then sent to the appropriate server.
-
The HTTP request is received by the web server and forwarded to the servlet container.
- The container maps this request to a particular servlet.
- The servlet is dynamically retrieved and loaded into the address space of the container.
-
The container invokes the
init()method of the servlet.- This method is invoked only when the servlet is first loaded into memory.
- It is possible to pass initialization parameters to the servlet so that it may configure itself.
-
The container invokes the
service()method of the servlet.- This method is called to process the HTTP request.
- The servlet may read data that has been provided in the HTTP request.
- The servlet may also formulate an HTTP response for the client.
-
The servlet remains in the container’s address space and is available to process any other HTTP requests received from clients.
- The
service()method is called for each HTTP request.
- The
-
The container may, at some point, decide to unload the servlet from its memory.
- The algorithms by which this decision is made are specific to each container.
- The container calls the servlet’s
destroy()method to relinquish any resources such as file handles that are allocated for the servlet; important data may be saved to a persistent store. - The memory allocated for the servlet and its objects can then be garbage collected.
Routing
Request Mapping
Customizing routes with the
Declaring HTTP request types
HTTP method specific shortcut variants of @RequestMapping:
@GetMapping@PostMapping@PutMapping@DeleteMapping@PatchMapping